Warsaw, 26 April 2022
Position of the Union of Entrepreneurs and Employers on the Consumer Credit Directive review
The European Commission has proposed a new Directive regulating consumer credit in June 2021.[1] The proposal is intended to replace the existing Consumer Credit Directive of 2008.[2] The draft rationale states that the current legal Act has not fully met its objectives, and therefore a revision is necessary. The aim is to introduce provisions that provide a clear legal framework for the financial industry’s economic activities and adapt regulations fit for the digital transformation. The rapidly expanding possibilities of electronic payments and socio-economic trends following it are causing consumers to change their habits in favour of the use of tools that have not yet been legally regulated.
The change in consumers’ behaviour necessitates an appropriate technological adaptation of financial products. This is due to the progressive digitalisation of commerce, payment methods and financial services. As a result, creditworthiness assessment mechanisms are often based on automated decision-making systems and products information is commonly provided in electronic form. The legislation aims to harmonise laws at the European level and strengthen consumer protection.
The Union of Entrepreneurs and Employers (ZPP) recognises the need to revise the provisions of the Consumer Credit Directive. We believe that it should create a legal framework that stimulates the development of the financial technology sector, which is undergoing significant changes and not make excessive barriers to the development and innovation of European businesses. Regulation should seek to strengthen consumer protection and increase consumer welfare in the digital environment through access to modern and secure digital tools. In our analysis of the proposal’s text, we identified several solutions in the draft that may be detrimental to the development of FinTechs in Europe and negatively affect the quality of available digital tools and consumer satisfaction with their use. In the following position paper, we set out our concerns regarding the revision proposal.
Buy-Now-Pay-Later
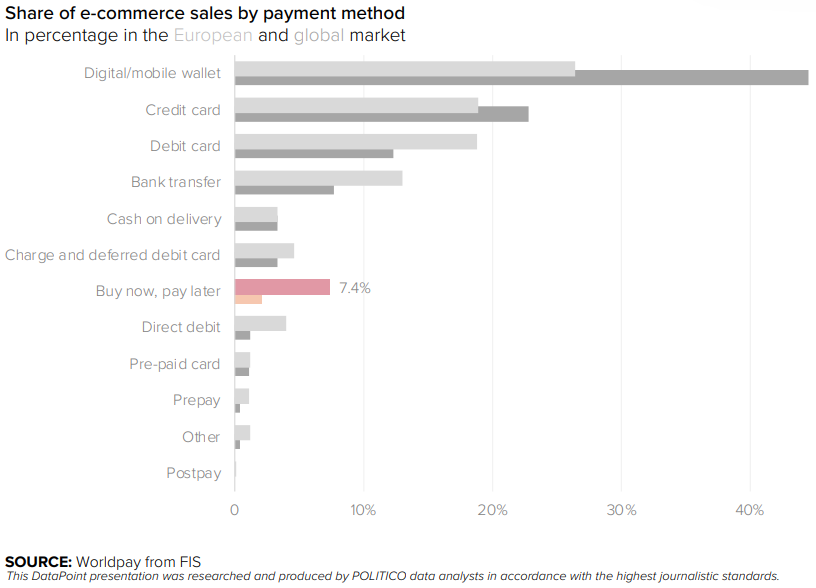
The development of FinTechs in Europe is very dynamic. There are already over 300 such companies in Poland, and the vast majority of them are young enterprises not older than 4 – 5 years.[3] The lack of regulations excessively limiting the use of modern digital tools is of great importance for the development of financial technology companies. Currently, the fastest-growing functionality in e-commerce is the ‘buy-now-pay-later. This enables the consumer to purchase online and pay later with no fee (or a very low fee). This instrument kicked off in Sweden and has become popular in Scandinavian countries. It is now rapidly gaining popularity in Europe as the e-commerce sector develops. The data presented shows BNPL’s share of the total e-commerce payment industry at 7.4 per cent of the European market, over 20 per cent share in the Swedish market and only four per cent lower share in the German market. This positions BNPL as an ordinary payment instrument for European consumers.

Access to secure financial services is beneficial to consumers and allows them to fulfil their daily needs. Low-interest (or interest-free) online loans are, as a rule, low-rate financial instruments. Therefore, they are not equivalent to high-value bank loans to purchase a house or a car. BNPL has a low risk of increasing consumer insolvency. BNPL operators offer many solutions to fit the product to the customer’s needs. However, the ability to create tailored offerings for customers may be limited due to disproportionate regulatory burdens on operators, which may lead to the creation of instruments that are unintuitive and incomprehensible to consumers.
Creditworthiness assessment
The creditworthiness requirements introduced by the proposed Directive should be customised to the type of financial commitment. The different lengths and costs of credit should determine the adequate assessment of credit risk in relation to the actual threat of insolvency. Socio-economic factors should influence the distinction between BNPL as a flexible payment option, loans with a high-interest rate or additional charges and products with a high commitment amount. Furthermore, e-commerce companies have their own reliable debt risk assessment systems based on online purchase history or credit fraud databases. This makes BNPL a low-risk service which should be reflected in the proposed Directive. In addition, it is a service characterised by immediate execution, so the traditional method of credit assessment based on manual verification of documents, such as income certificates, is inadequate for the needs of e-commerce and more costly than an assessment based on automated systems. Consumers may be reluctant to share their documents online, or it may prove too burdensome. As a result, this would be at the loss of FinTech companies and exclude some consumers from accessing credit tools.
Low-value loans
The current Act includes under the scope loans between €200 and €75,000. The proposed Directive extends its provisions to all loans with a value equal to or less than €100,000. This means that the Directive provisions will cover small purchases using BNPL.

Many BNPL users do not perceive this financing method as a loan. This is due to the tool’s flexibility, which can be tailored to the needs of a specific offer. It can take the form of a delayed repayment for a set period (e.g. 30 or 60 days), or it can be spread in instalment. Another possibility is to buy ‘on trial’ without making an immediate payment. Free trial shopping is complementary to the online shops’ free returns policies. The above makes it difficult for the consumer to associate BNPL with classic consumer credit. It is also not entirely clear how the different types of BNPL should be classified. Depending on the service provided, it can take the form of various contact obligations known to law.
Pre-contractual information obligations
Another factor that may negatively affect the development of innovative financial products may be the excessive pre-contractual information obligation enshrined in the draft Directive. FinTech products are becoming increasingly popular thanks to simple and transparent rules. This is a major difference from traditional banking products, burdened with restrictive information obligations. Loan amounts in BNPL are low and short-term, so there is no need to provide detailed information on held commitments.
Moreover, a large number of users purchase through mobile devices. Consequently, BNPL is also most commonly used for purchases via mobile phones or tablets. The introduction of a broad information obligation will result in the illegibility of the proposed offer. It may result in the unclarity of the service to the consumer’s detriment. In addition, it might lead consumers to give consent without knowing the actual terms of the agreement. This can lead to a dangerous situation called ‘consent-fatigue’. This is a phenomenon where the user is presented with a large amount of information to read and accept before using a product or service. A large amount of information shown causes a feeling of overwhelm on the consumer, who wants to use the tool as efficiently as possible without time-consuming familiarisation with voluminous information content. This psychological effect leads to a threat to the consumer’s attention who, accepting the rules without familiarisation, may fall prey to fraud and accept unfavourable conditions. This is a negative phenomenon resulting from a disproportionate information obligation on the operator. Considering the above, we believe that the increased information obligation will not benefit the consumers if an effective way of presenting and prioritising the information is not ensured.
In conclusion, we recognise the need to review consumer credit legislation and adapt it to the new demands of digital transformation. However, we note that specific provisions of the new Directive may halt the dynamic development of FinTech companies in Europe and be detrimental to consumers. Given the importance of consumer protection in the line with the case-law of the Court of Justice of the EU and the legislative activity of the European Institutions, there is no doubt that the welfare of consumers is a value that should be paramount when creating a new law. For this reason, we urge European legislators to consider the comments made above in order to make the provisions of the Consumer Credit Directive the most beneficial to the European economy.
***
[1] https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/default/files/new_proposal_ccd_en_3.pdf
[2] https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/PL/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32008L0048
[3] https://www.ican.pl/b/jak-wyglada-polski-fintech-rzut-oka-na-branze/PMQpOzRdk
See more: 26.04.2022 Position on the review of the Consumer Credit Directive

 ZPP Newsletter
ZPP Newsletter













