Warsaw, 15 May 2023
“Network fees” proposed by telecommunications operators – will consumers pay twice for infrastructure maintenance?
- Recommendations
Over the past months there has been an increased discussion regarding ETNO’s (European Telecommunications Network Operators’ Association – representing the biggest telecommunications companies) demands to charge content and application providers for the traffic that is generated by the use of their services. Telecoms believe that because of them they are being forced to bear the costs of infrastructure maintenance, and call content providers “stowaways” who do not contribute to the maintenance of European infrastructure. The truth, however, is quite different, and this is not a fight between telecoms and the big Internet giants, but a fight for the Internet as we know it. The concept of “fairshare payments,” as telecoms call them, is opposed by virtually all circles, except the largest Internet providers. Their introduction will certainly also be felt by Polish digital companies, which employ thousands of people and contribute greatly to the economy.
In this paper, we will present where the idea of introducing “fair share payments” came from and how it is argued. We will also present what effects the implementation of this solution will have on consumers and entrepreneurs, and we will present individual national circumstances.
In view of the ongoing debate on the introduction of “fair share payments” we note the following:
- Not even the telecoms themselves agree on the cost of handling Internet traffic. The Fédération Française des Télécoms presented an estimate according to which handling network traffic generates €2 billion in costs in France, or €27 for each resident of the country. That’s a third of the amount of €80 per EU resident calculated by ETNO, and it’s still significantly inflated.
- The research indicates that South Korea is so far the only country that has responded to the concerns of telecoms and introduced the legal billing rule of Spending Party Network Pays (SPNP). Under the rules, Internet content and application providers have been required to pay fees to telecoms. The report’s conclusions are clear. All of these regulations have led to a reduction in the quality and variety of content on the Internet. It is also expected to increase costs for the end user of content and reduce investment in local infrastructure
- Fair share payments can lead to a deterioration in the quality of online content offered by providers. Additional fees mean a reduction in budgets for creating quality services offered to consumers.
- The introduction of additional fees will lead to a competitive imbalance in the telecom market itself favoring the largest players. They will lead in practice to the strengthening of oligopolies in the market.
- Fair share payments are widely criticized by almost all circles except the largest telecoms. Experts point out that among the numerous disadvantages of this solution, the most noteworthy is the violation of the principle of Internet neutrality.
- In Poland, the expansion of Internet infrastructure is carried out with massive public funding. This means that this purpose is financed by all taxpayers. One can point, among others, to the information contained in the “Broadband Access Plan for Poland,” according to which in the Digital Poland Operational Program for 2014-2020, out of the total funds amounting to 2.57 billion euros, over a billion was allocated to the expansion of broadband networks.
In view of the above, we urge to reject the idea of introducing “fair share payments” within the European Union.
- Proposals to introduce so-called “fair share payments”.
For nearly a year there has been a discussion on the idea of introducing so-called “fair share payments”. This idea was presented by Commissioner Vestager on May 2, 2022[1]. Unfortunately, all indications are that the European Commission is seriously considering the introduction of fair share payments for Internet content and application providers. The issue is being highlighted as a dispute between two big industries, Internet access providers (telecoms) and big Internet corporations. The issue has come to the fore through ETNO’sactivities , which is extensively lobbying for the introduction of fees for “extraordinary growth in Internet traffic that generates challenges for sustainable investment in the European network.” This position is supported among others by Deutsche Telecom, Orange, Telefonica and Telecom Italia, claiming that the six largest Internet content providers account for more than half of Internet traffic[2]. The argument, in a nutshell, is that large US corporations generate heavy network loads by offering their content, and this leads to the need for large infrastructure expenditures. This traffic is generated by the popularization of streaming, teleconferencing, remote learning, social media, and cloud services. Telecoms assume that since annual network maintenance in 2020 cost €52.5 billion, and service and application providers account for 60-70% of Internet traffic, they should pay €36 billion (€80 per EU resident) to telecoms. Moreover, this amount should increase every year due to the growth of network traffic[3].
However, the telecoms’ argument is fraught with a number of significant problems. First of all, telecoms charge consumers themselves for internet use. Their demands on service and application providers are nothing more than a demand for a second fee for the same service.
This relationship is illustrated by the graph below:
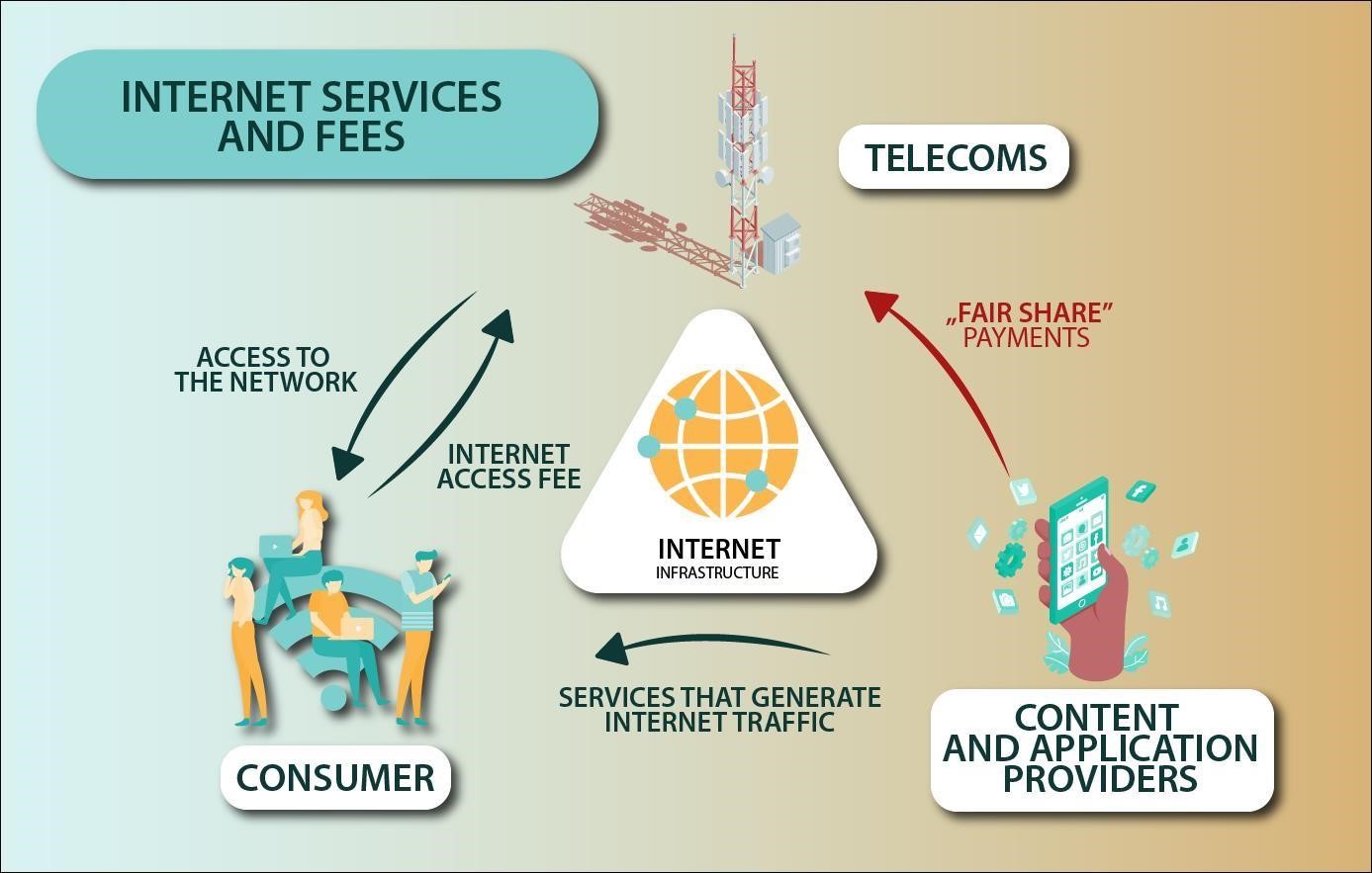
Telecoms make their infrastructure available to consumers. Consumers use internet content offered by service providers and applications, and this generates traffic on the network. As the use of content available on the Internet generates traffic, telecoms have decided to demand an additional fee from service and application providers called “fair share payment.”.
What is also worth noting is that telecoms argue for their demands with the need to maintain the network due to increased traffic (load). Meanwhile, telecoms’ investments consist of relay stations, fiber optics, modems, and data centers, among other things. A large cost is, for example, the construction of masts and fiber-optic networks. Nevertheless, 70-80% of the total telecom costs are spent precisely on infrastructure, which lasts and can be successfully used for at least 30 years. The remainder relates outdated equipment, which should be upgraded every 5-10 years. The cost of “network maintenance” due to high traffic is therefore not high, and this is explicitly admitted by some telecoms. The Fédération Française des Télécoms presented an estimate according to which handling network traffic generates 2 billion euros in costs in France, or 27 euros for each resident of the country. That’s a third of the amount of €80 per EU resident calculated by ETNO, and it’s still significantly inflated. In France, you can easily find consumer offers of 10 gigabit-per-second connections along with phone and TV at prices around 30-49 euros per month[4]. These package offers are also a great example of existing interrelations and co-dependencies between telecommunications operators and service providers. In Poland, Orange offers fiber optics with 1 Gbps download speeds for 17.5 euros per month[5]. It is also worth citing an example in which one German student accommodation organization wanted to provide students with Internet access at a speed of at least 1 Gbps at all times in 2020. The offer for such access was made by 8 German telecoms, of which 5 offered the amount of 11 euros per month per student[6]. These examples indicate market prices for Internet access, no Internet provider would bid below its costs. Hence, the calculations of both ETNO and the Fédération Française des Télécoms are clearly inflated. It is also difficult to argue that internet platforms are “free riders” because they have invested billions in the construction and development of internet infrastructure over the last decade.
- Effects of “fair share” fees on citizens and businesses.
A fee similar to “fair share payments” has been introduced in South Korea, and this is basically the only case where we can find similarities with existing solutions. The Korean example has been studied by BEUC (The European Consumer Organization), among others. It cited a study commissioned by the German Federal Internet Agency. The research indicates that South Korea is so far the only country that has responded to the concerns of telecoms and introduced the legal billing rule of Sending Party Network Pays (SPNP). Under the rules, Internet content and application providers have been required to pay fees to telecoms. The report’s conclusions are clear. All of these regulations have led to a reduction in the quality and variety of content on the Internet. It is also expected to increase costs for the end user of content and reduce investment in local infrastructure[7].
A similar view is held by the European Internet Exchange Association, which, analyzing, among other things, the situation in South Korea, points out that “fair share payments” are detrimental to the proper functioning of the Internet communications and peering market and distort competition in this market. In addition, they will negatively affect the experience of citizens in basic business operations, data sharing, access to cloud services and the development of research projects[8] .
Paradoxically, therefore, “fair share” fees in Korea have had exactly the opposite effect of the one that telecoms claim they were intended to serve. It should be pointed out that the introduction of additional fees on Internet content providers could force them to introduce at least partial payment for their services, which were previously free. This could reduce access to online content and lead to digital exclusion of less affluent Internet users. This straightforwardly violates the principle of Internet neutrality, which, however, by definition says that it is the ability of all Internet users to access selected content and applications.
Another issue is the reduction in the quality of content available online. Clearly, many companies offering, for example, streaming services, access to online TV or other video content will be affected by such fees. Prices for access to content can be introduced here or raised only up to a certain level, above which consumers will not be able to accept additional fees. In practice, it will be impossible to pass on the entire cost to content consumers. This means a smaller budget for the creation of quality online content. Similar concerns are presented, among others, by the European Association of Commercial Television and VoD Services, which has issued an open letter expressing concern on the introduction of network fees and its’ effects on the European creative industry[9]
Crucially, the dispute over “fair share payments” should not be viewed as a conflict between big telecom companies and big Internet corporations. These fees have the potential to very seriously undermine competition on the Internet and threaten the smallest entrepreneurs. Such concerns are presented by the French Association of Alternative Telecom Operators, among others, which notes that fees of this kind will be fatal to the survival of small and medium-sized digital companies[10]. Small companies offering content on the Internet will be put in a very difficult position, as on the one hand they will be charged for Internet traffic, and on the other hand it will be difficult for them to pass this cost on to consumers. The introduction of fees to offset the cost of “fair share” fees will make them lose their competitiveness with larger players in the market.
What’s more, smaller telecom service companies are also openly criticizing the idea of fees. Such threats are pointed out by both MVNO Europe and the EU Competitive Telecommunications Association (ECTA). They point out that the fees will cause serious damage to competition in the telecom market, will directly affect smaller operators, and will negatively impact both individual consumers and telecom customer companies. The fees will only benefit the largest players in the market by strengthening their oligopolies[11] .
“Fair share payments” are also criticized by academics. In October 2022, they sent a letter to the European Commission signed by 29 market experts, PhDs and professors who know the market very well. They pointed out that the proposal to charge Internet service providers and applications is not new and has always been rejected as harmful. They point out that for the past decade the idea has been unequivocally criticized by experts, business and NGOs. The experts point out in their letter that in 2015[12], the EU granted internet users the right to freely access information and content, use and deliver applications and services of their choice. EU standards require broadband service providers to treat data in a non-discriminatory manner, regardless of what it contains, what application transmits the data, where it comes from and to whom it is directed. Even if fair share payments were directed only to the largest Internet content providers, this would still directly violate open Internet access standards.
Experts also point out that broadband networks are an important part of the value chain just as Internet content providers are driving demand from Europeans for access to the Web. Broadband providers gain significant benefits from the fact that service providers generate demand for broadband access. In doing so, telecoms pay nothing for the efforts of Internet content and application providers in creating that demand. Without the demand generated by Internet content providers, telecoms would not have many customers for high-speed Internet access services. Customers who, after all, pay telecoms for that access. Moreover, governments, universities, government offices and other public entities are also Internet content providers. All of these entities are already paying for the development of Internet networks. The researchers also explicitly point out that history and economic theory indicate that similar fees will not increase investment in Internet infrastructure by telecoms[13].
The European Video on Demand Coalition is also opposed to “fair share payments,” pointing out that the introduction of this fee will harm the development of innovation in Europe and the digitization process. They also express concern that proposals of this kind are being put forward without adequate public consultation and analysis of the impact of such solutions[14]. Germany’s VAUNET argues that fees threaten media pluralism and the quality of content[15], while the Association of Commercial Television points out that Internet access fees for content providers mean less money for content creation. Which will ultimately lead to less or lower quality content[16].
Finally, it should be noted that on June 8, 2022. 34 social organizations from 17 countries sent an open letter to Commissioners Vestager and Breton pointing out the problems cited above and opposing the introduction of “fair share payments.” The authors of the letter emphasize that the Commissioner’s statement about players generating a lot of Internet traffic who should be charged a fair fee to telecoms shows a fundamental misunderstanding of how the Internet works[17].
So it turns out that both businesses (including smaller telecoms), social organizations, industry organizations and academia speak with one voice and strongly oppose the idea of “fair share payments” stressing that it is harmful to the entire market. The only entities that will gain from it are the largest telecoms, which are actively lobbying the solution at the European Commission.
- Polish market
The value of the Polish telecommunications market is 40.8 billion Polish zlotys (approximately 8.73 billion euros). Telecommunications investments in 2020 amounted to 8.9 billion Polish zlotys (approximately 1.95 billion euros). As many as 66.6% of broadband internet users have a connection with a bandwidth of at least 100 Mbps, and estimates indicate that by 2026, over 80% of mobile internet users will have access to 5G technology[18].
According to a survey conducted by the Office of Electronic Communications on a sample of 2011 people aged 15 and over, 97.2% of people in our country use mobile phones, 54.9% use mobile internet, and 54.1% use stationary internet. Any kind of internet access was declared by 79.1% of the respondents. The average monthly bill for stationary internet is 59.17 zlotys (just under 13 euros), while for mobile internet it is 46.43 zlotys (approximately 10 euros)[19]. Poland ranks 30th in the Speedtest Global Index for broadband internet access speed, with an average speed of 106.40 Mbps, and 44th for mobile internet with a speed of 47.86 Mbps[20]. Therefore, the internet in Poland is relatively fast and inexpensive.
Providing fast internet at a relatively low cost, of course, requires investment in infrastructure. However, in Poland, a number of such tasks are undertaken from public funds and do not cost telecom companies a penny. One can point, among others, to the information contained in the “Broadband Access Plan for Poland,” according to which in the Digital Poland Operational Program for 2014-2020, out of the total funds amounting to 2.57 billion euros, over a billion was allocated to the expansion of broadband networks[21]. Further expenditures are planned in the program for 2021-2027. The entire 2 billion euros is to be allocated, among other things, to ensure access to broadband internet with a speed of at least 100 Mbps in every household and business and with a speed of at least 1 Gbps in every place that is significant in terms of social and economic aspects, such as schools, hospitals, offices, and technological and business centers[22]. In addition, funds for the expansion of internet infrastructure have also been planned in the Broadband Fund, which will finance investment projects worth a total of 20 million zlotys in the first call[23]. Further financing has also been planned in the National Recovery Plan. Formally, 21% of the budget is allocated for digitization-related projects, although Minister Plenipotentiary Paweł Lewandowski suggests that even over 30% of the NRP budget may be allocated to this purpose. By 2026, 931 thousand households are planned to be connected to broadband networks[24].
Taking into account the scale of public investments in expanding internet infrastructure, it is clear that the largest cost associated with the dissemination of fast internet in Poland has been to a large extent supported by public funding, mainly through funds from the EU. Similarly, in other countries, huge amounts of money from both the EU and national budgets are allocated for digital transformation. Therefore, telecom companies are not bearing these costs, but rather taxpayers. This means that big telecommunication companies are using infrastructure financed by all of us, burdening their customers with the costs of internet access, and now they are demanding “fair share payments” from content and internet application providers, which could result in significant changes to the internet as we know it, unfortunately only for the worse. Telecom companies will gain by receiving enormous amounts of money, while we will all lose.
In addition, other instruments such as the Broadband Fund are being prepared or already launched, and the development of telecommunications infrastructure is included in the National Recovery Plan.
Therefore, it is difficult to find rational reasons for additional funding of telecommunication operators’ budgets. Moreover, the adoption of the proposal on network fees may in practice lead to limiting access to certain platforms, which directly contradicts the principle of net neutrality.
***
[1] https://www.reuters.com/business/media-telecom/eus-vestager-assessing-if-tech-giants-should-sharetelecoms-network-costs-2022-05-02/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[2] https://www.reuters.com/technology/eu-wants-details-big-tech-telcos-investment-plans-source-2023-01-10/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[3] https://www.project-disco.org/european-union/020123-fast-internet-doesnt-cost-eu-telecom-operatorsmuch-at-all/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[4] https://www.project-disco.org/european-union/020123-fast-internet-doesnt-cost-eu-telecom-operatorsmuch-at-all/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[5] https://oferty.orange.pl/swiatlowod2/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[6] https://www.project-disco.org/european-union/020123-fast-internet-doesnt-cost-eu-telecom-operatorsmuch-at-all/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[7] WIK-Consult report, Study for the Federal Network Agency Germany, Competitive conditions on transit and peering markets Implications for European digital sovereignty Final report.
[8] https://www.euro-ix.net/media/filer_public/c7/72/c772acf6-b286-4edb-a3c5042090e513df/spnp_impact_on_ixps_-_signed.pdf (dostęp na dzień 27.04.2023 r.).
[9] https://www.acte.be/publication/tv-vod-statement-on-network-fees/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[10] https://www.project-disco.org/european-union/020723-is-anyone-in-favour-of-taxing-internet-traffic/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[11] https://www.project-disco.org/european-union/020723-is-anyone-in-favour-of-taxing-internet-traffic/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[12] Regulation (EU) 2015/2120 of the European Parliament and of the Council of November 25, 2015, Official Journal of the European Union L 310.
[13] https://www.komaitis.org/personal-blog/29-internet-experts-and-academics-send-a-letter-to-thecommission-urging-to-abandon-the-sending-party-network-pays-proposal (accessed April 27, 2023).
[14] https://www.europeanvodcoalition.com/positions/position-paper-on-net-neutrality/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[15] https://www.politico.eu/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/02/VAUNET-positionpaper_NetworkFees.pdf (accessed April 27, 2023).
[16] https://www.acte.be/publication/tv-vod-statement-on-network-fees/ (accessed April 27, 2023).
[17] https://epicenter.works/sites/default/files/2022_06-nn-open_letter_cso_0.pdf (accessed April 27, 2023).
[18]https://www.telepolis.pl/images/2022/06/raport_o_stanie_rynku_telekomunikacyjnego_w_polsce_w_2021_r._30.06..pdf (accessed April 27, 2023).
[19] Office of Electronic Communications, Analysis of the functioning of the telecommunications services market in Poland and assessment of consumer preferences. 2022. Survey of individual customers.
[20] https://www.speedtest.net/global-index (accessed April 27, 2023).
[21] https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/broadband-poland (accessed April 27, 2023).
[22] https://www.gov.pl/web/funds-regional-policy/nearly-2-billion-euros-for-polands-digital-transformation (accessed April 27, 2023).
[23] https://www.gov.pl/web/cyfryzacja/fundusz-szerokopasmowy–pierwszy-nabor-wnioskow (accessed April 27, 2023).
[24] https://www.wirtualnemedia.pl/artykul/internet-szerokopasmowy-rozwoj-sieci-budzet-kpo ; https://www.gov.pl/web/planodbudowy/transformacja-cyfrowa (accessed April 27, 2023).
See more: 15.05.2023 “Network fees” proposed by telecommunications – operators will consumers pay twice for infrastructure maintenance?

 ZPP Newsletter
ZPP Newsletter














Recent Comments